Overview of the Carbide Tooling Industry
The carbide tooling industry has witnessed significant growth over the past several decades. This growth is in part due to advancements in technology and the increasing need for precision in manufacturing processes. Cutting tools embedded with carbide inserts are prominently featured in various industries, ranging from automotive and aerospace to woodworking and metalworking. These specialized tools are sought after for their ability to maintain sharpness and enhance production efficiency.
Increasing Popularity and Market Trends

The popularity of carbide inserts has skyrocketed due to their superior performance and durability. Market trends show a rising demand for these tools as manufacturers seek ways to minimize downtime and improve productivity. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global market valuation for carbide cutting tools was estimated to reach around USD 23 billion by 2028. This upward trend is further accelerated by the increased adoption of automated and precision-based machinery.
Addressing Demand and Supply Challenges
Despite their growing popularity, the carbide tooling industry faces supply chain challenges. Factors such as the limited availability of raw materials and the complexity of production processes contribute to supply constraints. To address this, many companies are investing in new technologies and processes to improve efficiency and reduce production costs. In addition, collaborations between suppliers and manufacturers are becoming increasingly vital to ensure a steady supply of high-quality carbide tools.
Market Dominance of Carbide Tools
Carbide tools have established a dominant position in the cutting tools market. Their robustness and versatility are key drivers of this dominance, outperforming traditional cutting tools in various applications. With the evolution of carbide technology, these tools now cater to a wider range of materials, including hard metals and composites, further solidifying their market presence. The ability to provide consistent, high-quality finishes and withstand rigorous manufacturing conditions has cemented carbide tools as an industry standard.
What is Carbide?
To fully appreciate the advantages of carbide inserts, it is essential to understand what carbide is. Carbide is a chemical compound composed of carbon and a more electropositive element, often used in industrial applications due to its hardness and resistance to wear.
Definition and Composition
Carbide, in its simplest form, is a compound in which carbon is combined with a metallic or semi-metallic element. This combination creates an ultra-hard material that is capable of cutting through tough surfaces with precision. The hardness of carbide materials is typically measured on the Mohs scale, where they score significantly higher than other common industrial materials.
Essential Element and Chemical Compound

Carbides are classified as interstitial compounds since carbon atoms fit into the interstices, or gaps, in a metallic lattice. This structure gives carbide compounds their characteristic hardness and durability. The most widely used type of carbide in cutting tools is tungsten carbide, favored for its unmatched toughness and longevity.
Common Combinations with Carbide
Calcium Carbide
Calcium carbide is primarily used in the production of acetylene gas and as a reducing agent in metal production. Despite being less commonly associated with machining, it plays a crucial role in various industrial processes.
Aluminum Carbide
Aluminum carbide is often used in laboratory and research settings due to its unique properties. It’s a valuable material for the production of certain specialty alloys and in the preparation of certain chemicals.
Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide, another vital form of carbide, stands out for its thermal conductivity and semiconductor properties. It is used extensively in high-temperature applications such as furnace linings and abrasives.
Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is the most prominent form of carbide used in cutting tools, thanks to its superior hardness and exceptional wear resistance. Composed of tungsten and carbon, this compound’s durability makes it ideal for applications that involve heavy-duty cutting and machining. Tungsten carbide inserts can significantly extend tool life, reducing the frequency of tool changes and maintenance.
Iron Carbide
Iron carbide, formed by the combination of iron and carbon, is commonly used in steel manufacturing. Although it is not as hard as tungsten carbide, it still offers considerable hardness and is often utilized in creating wear-resistant surfaces in the steel industry. Its structural stability and effectiveness in improving the hardness of steel make it a valuable component in various industrial processes.
Comparison Between Carbide and HSS Tools
Overview of High-Speed Steel (HSS) Tools
High-speed steel (HSS) tools were once the industry standard for cutting tools, favored for their hardness and ability to retain their cutting edge at high temperatures. Composed primarily of carbon steel with the addition of other elements like tungsten, chromium, and vanadium, HSS tools are still used in many machining applications. They offer good toughness and are relatively resistant to chipping.
Popularity of Carbide Tools over HSS
Despite the longstanding use of HSS tools, carbide tools have gained traction due to their superior performance. The shift toward carbide tools over HSS is driven by their enhanced cutting ability and longer life span, particularly in high-stress environments.
Performance and Efficiency Comparisons
Carbide tools outperform HSS tools in terms of speed and precision. They can operate at much higher cutting speeds, allowing for faster material removal and reduced machining times. Moreover, carbide inserts maintain their cutting edge longer than HSS, ensuring consistent performance over extended periods. This efficiency translates into higher productivity and better surface finishes on machined parts.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
While the initial cost of carbide tools may be higher than that of HSS tools, the longer tool life and reduced downtime for tool changes make carbide tools a more cost-effective choice in the long run. Investing in carbide tools can lead to significant savings in manufacturing costs, as the need for frequent replacements diminishes.
Benefits of Carbide Tools
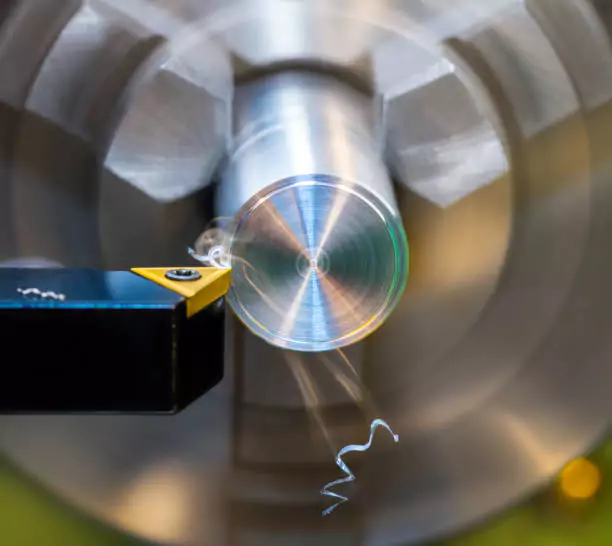
Affordability and Effectiveness Compared to HSS Tools
Carbide tools, although initially more expensive, offer greater affordability in terms of their overall life cycle costs. Their resilience and durability translate into fewer replacements, thus reducing operational expenses. When considering the longer tool life and consistent performance, carbide tools present a more economical option compared to HSS tools in high-production environments.
High-Temperature Endurance
Carbide tools exhibit a remarkable capacity to withstand high temperatures without losing their hardness. This high-temperature resistance allows for more aggressive cutting parameters, which in turn leads to higher productivity. In contrast, HSS tools tend to soften under extreme heat, compromising their effectiveness over time.
Durability and Longevity Features
Resistance to Wear and Tear
One of the standout features of carbide inserts is their exceptional resistance to wear and tear. Carbide’s inherent hardness allows the tools to endure the rigors of cutting through hard materials, maintaining their structural integrity far longer than HSS tools. This resistance to wear reduces the need for frequent tool changes, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
Longer Shelf-Life Advantages
The longevity of carbide tools is another significant advantage. These tools are designed to last longer, providing consistent performance even after extended use. Their longer shelf-life means that manufacturers can rely on carbide tools for prolonged periods without compromising on the quality of the cuts and finishes.
Performance Quality Enhancement
Improved Finish and Surface-Finish Quality
Carbide inserts are known for providing superior finishes on machined parts. The hardness of carbide allows for cleaner cuts and smoother surfaces, which is critical in applications where precision and aesthetic quality are paramount. This improved finish quality reduces the need for secondary operations, such as grinding or polishing.
Consistent Cutting Edge Retention
Carbide tools maintain a sharp cutting edge longer than HSS tools, ensuring consistent performance. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in automated machining processes where maintaining precision and reliability is crucial. Consistent cutting edge retention leads to enhanced product quality and fewer reworks.
Cost-Effectiveness and Resilience Aspects
Lower Overall Cost Analysis
While the upfront cost of carbide tools is higher, their extended lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements offer a lower overall cost of ownership. Manufacturers experience cost savings through fewer tool replacements and reduced downtime, making carbide tools a financially sound investment.
Resistance to Cracking Considerations
Carbide tools exhibit excellent resistance to cracking and chipping, making them robust choices for challenging machining environments. This resilience ensures that the tools can withstand the stresses of high-speed operations and heavy-duty cutting without suffering structural failures, contributing to their longevity and reliability.
Industry Popularity
Preferred Choice for CNC and Lathe Machines
Carbide inserts are the preferred choice for CNC and lathe machines due to their precision and durability. These tools enable high-speed, accurate machining, making them indispensable in automated manufacturing setups. Their ability to produce consistent results while minimizing tool wear and maintenance requirements makes them ideal for CNC applications.
Versatility and Diverse Application Fields
The versatility of carbide tools allows them to be used in a diverse range of industries, from automotive and aerospace to medical device manufacturing and general engineering. Their performance in cutting various materials, including metals, composites, and wood, underscores their adaptability and broad application scope.
Summary of Advantages and Future Prospects in the Carbide Tooling Industry
Carbide inserts offer numerous advantages over traditional cutting tools like HSS, including superior performance, longer life spans, and cost-effectiveness. Their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist wear and tear makes them ideal for high-production environments. As technology advances and the demand for precision machining grows, the carbide tooling industry is poised to expand further.
Manufacturers increasingly rely on carbide tools to meet the challenges of modern production processes. By investing in these advanced cutting tools, industries can achieve greater efficiency, enhanced product quality, and reduced operational costs. The future of the carbide tooling industry appears promising, with ongoing innovations set to further enhance the capabilities and applications of carbide inserts.



